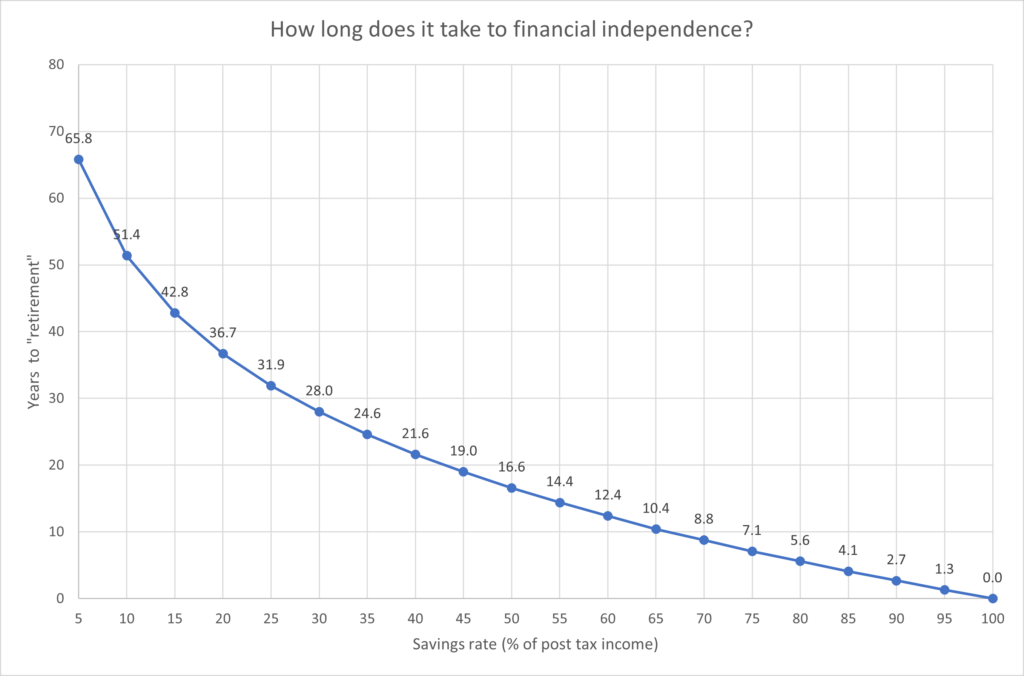
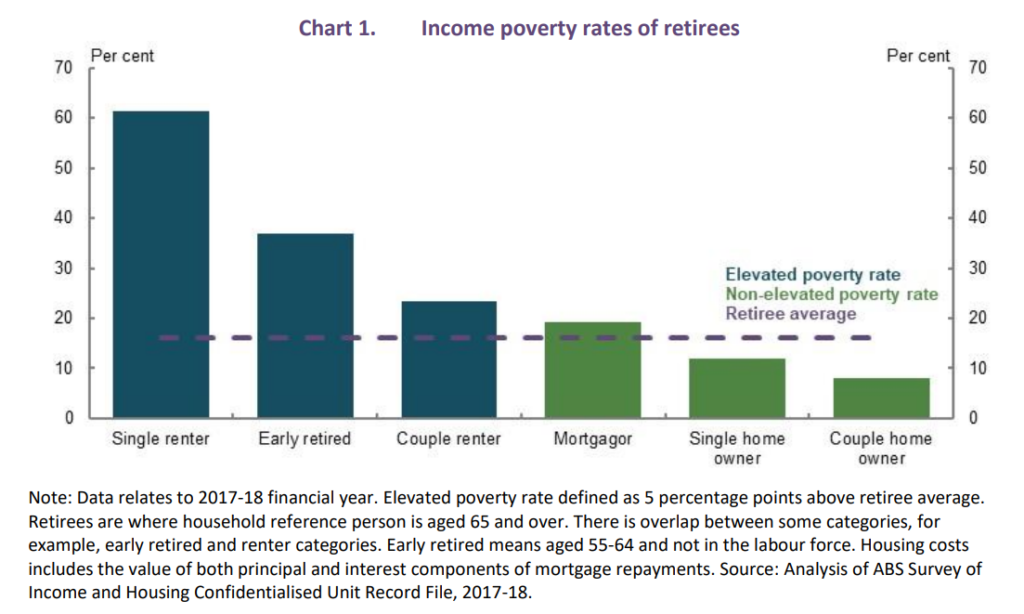
After discussing how hard it is for those trying to buy their first home. Slack Investor is compelled to provide some hope in the desire to own your home before you retire. The numbers are in … and, not owning a house in retirement or, losing your job before you retire, puts you at real risk of not reaching a comfortable financial position.
Whereas very few retired home owners are in poverty, most retired renters are …
Helen Hodgson – Professor, Curtin Business School
There are very few existing incentives on the dusty twisted road to home ownership. They include Stamp Duty exemptions/concessions that vary from state to state. In Victoria, they are available for homes less than $750K. There is also the First Home Buyers Grant (FHBG), which, again, is dependent on which state you live. In Victoria, that comes in at a measly (but I’ll take it!) $10K.
All of these things are worth considering and applying for when you finally purchase a home, but the First Home Super Saver Scheme (FHSSS) is a lesser known arrangement that seems to make sense – but it requires a bit of “setting up”.
In order to make the most of the FHSSS, you’ll need to start planning well ahead of the time to buying a house/apartment (3 – 4 years?) – But planning ahead is the very trait that Slack Investor loves!
First Home Super Saver Scheme (FHSSS)
I did refer to the First Home Super Saver Scheme (FHSSS) way back in 2017 when it was just a twinkle in ScoMo’s eye – it started as an election promise to get the “young folk” on board as the government felt a need to at least be seen to be doing something to help first homeowners.
Normally, your super is a beautiful one-way savings vehicle where your retirement money is locked away, and compounding, until you meet a condition of release or, when you reach your preservation age. For most people, the big taxation benefits kick in after the age of 60 – but that’s another story.
However, the treasure chest of the FHSSS, is opened when you first start to make some extra super contributions (up to $15K per year).

These voluntary contributions can be withdrawn from your super when you finally ready to purchase a home – by filling out an ATO form for a ‘determination’. The determination will tell you exactly how much you can withdraw – it will be a little more than you have put in (your contributions – up to $50K – plus deemed earnings)- and waiting a month.
Getting the money out usually takes 15–25 business days … once you withdraw money to buy a house, you have one year to use it
Choice – First Home Super Saver Scheme: Can it help you get on the property ladder?
These extra contributions are over and above the compulsory super that your employer makes. The scheme works by making an arrangement with your paymaster to salary sacrifice into your super – up to $15K per tax year. Contributions can also be made by arranging with your super provider to make a personal super contribution.
The tax savings come about as, you only pay 15% tax on these super contributions – rather than your marginal rate of say, 32.5%. Plug in your own details into this calculator to determine your possible tax savings.
There are complexities and limitations that include not exceeding your concessional contribution cap of $27,500 – but your super provider will help here.
I would recommend all prospective home owners to take a look at this scheme. Assessment for eligibility is made on an individual basis … so couples and friends can combine their amounts – but start now – it will take a few years to get a useful house deposit.
Colonial First State outline a case study of a couple that have each started voluntary extra super contributions of $15K – After 15% tax this comes down to $12 750 p.a of contributions into their funds. After 4 years, they each have amassed $55K (4 x $12 750 plus deemed interest). A combined house deposit of $110K was possible using the FHSSS – and, using a favourite Slack Investor way of saving – deductions from your salary before you even see it! All of this with tax advantages.
Homework (get it!): – Potential homeowners – read about it – and get on the FHSSS!